Eggs have long been an essential part of people’s daily diets, and as consumption continues to rise, so does the demand for effective packaging solutions. Egg trays and cartons play a vital role in ensuring eggs reach consumers safely, protecting them from damage while maintaining hygiene. This article explores the role of pulp molded egg trays, structural market trends, and operational challenges within the global egg tray industry.
Functional Importance of Pulp Molded Egg Trays

Operational Support Across the Egg Supply Chain
Pulp molded egg trays play a foundational role in the global egg industry by acting as a critical interface between production, logistics, and market distribution. At an operational level, they provide structural protection for fragile eggs, enabling efficient handling, stacking, and transportation across increasingly complex supply chains.
Economic Value in High-Volume Egg Distribution
From an economic perspective, egg trays help control breakage rates and logistics costs, directly influencing profitability for producers and distributors operating at high volumes and thin margins. Their standardized form also supports automation in grading and packing facilities, improving overall system efficiency.
Contribution to Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Equally important, pulp molded egg trays support industry sustainability goals. Manufactured mainly from recycled paper and fully recyclable, they meet regulatory requirements and market preferences for fiber-based packaging, reinforcing their role as long-term infrastructure within the global egg industry.
From Poultry Farm to Consumer: Egg Packaging and Logistics
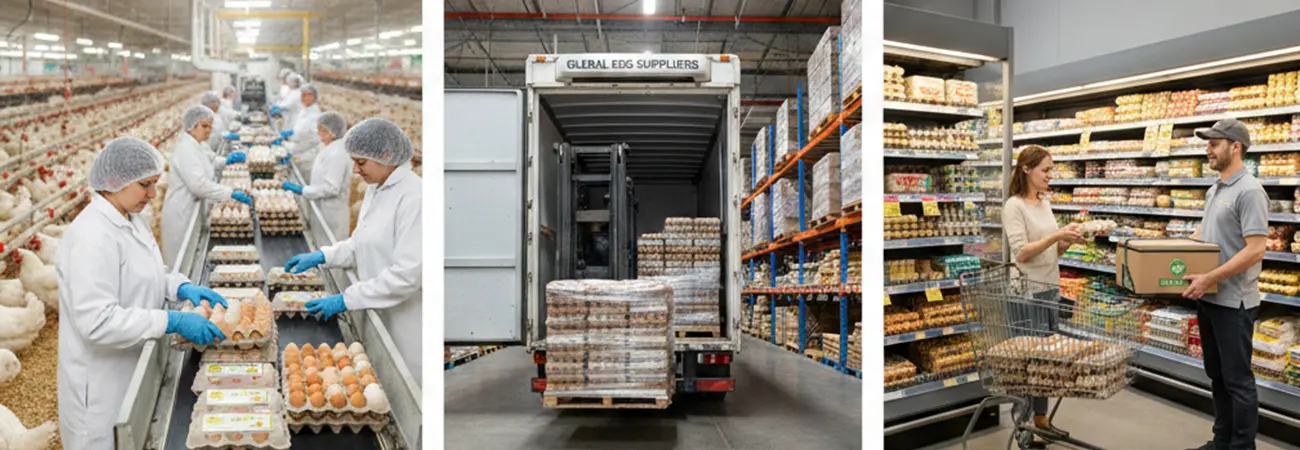

From Farm to Consumer
Eggs pass through a complex supply chain before reaching consumers. The process begins at poultry farms, where eggs are collected and sorted based on size and quality. These eggs then move to grading and packing facilities, where they are carefully inspected and placed into trays or cartons designed to minimize breakage.
Wholesale Distribution
Once packed, eggs are transported to wholesalers, who supply supermarkets, local markets, and restaurants. During this stage, packaging must withstand long-distance transportation and stacking in storage, ensuring that eggs remain intact.
Retail and Consumer Delivery
Retailers receive eggs and display them for sale, often in consumer-friendly cartons that offer both protection and convenience. For eggs sold online or through delivery services, additional protective measures may be added to prevent damage during shipping.
Structural Drivers Behind Rising Egg Tray Demand
The demand for egg trays has grown not only in volume but also in complexity. Several structural factors are reshaping how egg packaging is specified and produced.

Growth in Egg Production Volumes
Global egg production has increased steadily over the past decade, driven by population growth and rising protein demand. Higher output naturally translates into higher packaging consumption. However, scale introduces sensitivity: a marginal reduction in breakage rates can represent substantial economic savings when millions of eggs are handled daily.
Expansion of Distribution Radius
Egg distribution is no longer limited to short-distance regional markets. Improvements in cold chain logistics and transport infrastructure have extended delivery distances. Longer transport routes increase exposure to vibration and stacking pressure, raising the performance requirements for egg trays.
Automation and Standardization
Modern grading and packing facilities increasingly rely on automated systems. These systems demand egg trays with consistent dimensions, stable wall thickness, and predictable mechanical strength. Variability that was once tolerated in manual operations now leads to operational friction.
Transition Toward Fiber-Based Packaging
Environmental regulations and retailer sustainability commitments are accelerating the shift away from plastic packaging. Pulp molded trays, made primarily from recycled paper, align with circular economy principles and are widely accepted in both domestic and export markets.
Global Market Overview of Pulp Molded Egg Trays
The pulp molded egg tray segment is a major part of the global egg packaging market, driven by rising egg production and growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. According to industry reports, the egg tray packaging market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1.9 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of about 4.8 % over the period. Molded pulp trays accounted for the largest share of this segment due to their cost-effectiveness, biodegradability, and protective performance for fragile eggs.
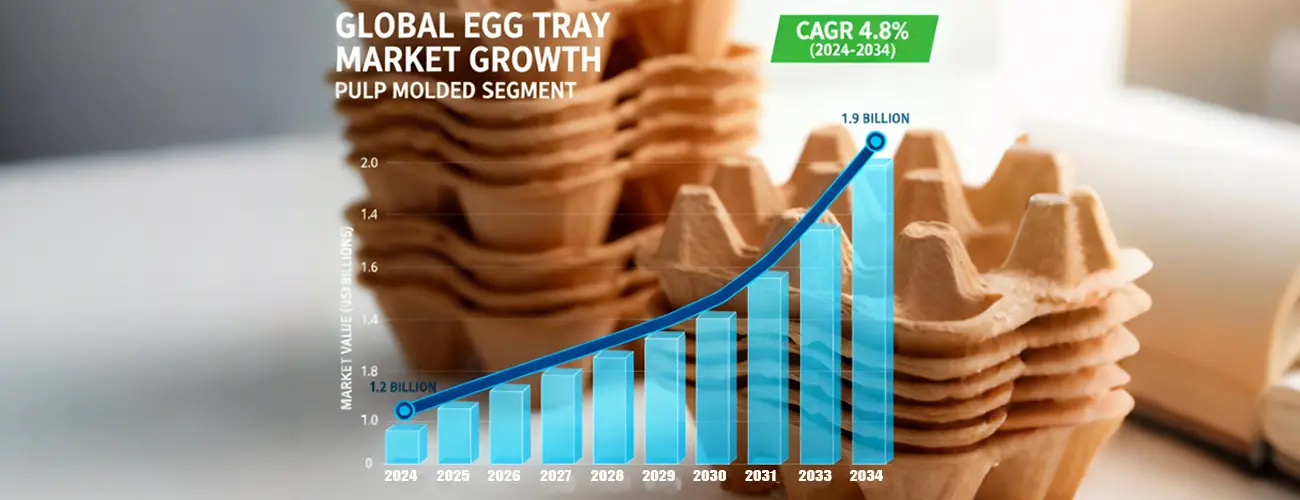
Market Characteristics
High-volume & Low-margin Product
The egg tray market is characterized by large production volumes where efficiency directly impacts profitability.
Regionally Distributed Demand
Demand closely follows local egg production trends. Asia‑Pacific, particularly China and India, drives the majority of consumption, while Europe and North America maintain steady replacement and upgrade demand.
Stable Long-term Growth
The market growth is aligned with consistent food consumption rather than discretionary spending. For example, global egg packaging demand is expected to reach nearly USD 13 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of over 6 %.
Emerging Markets Opportunities
Asia, Africa, and Latin America are experiencing rising egg consumption, creating strong demand for localized production capacity of pulp trays.
Industry Challenges and Operational Opportunities
The pulp molded egg tray industry faces several operational challenges that directly influence production efficiency, product quality, and sustainability.
Maintaining Tray Consistency and Strength
Variations in raw material quality and drying conditions can lead to inconsistent tray geometry and weak structural integrity. Even minor deviations can increase egg breakage during transportation, causing economic losses for distributors and retailers. Ensuring uniform strength across high-volume production lines remains a critical operational challenge.
Meeting High Throughput and Quality Standards
Producers are under pressure to increase output without compromising tray uniformity. Manual operations or poorly integrated lines often result in dimensional inconsistencies, slowed production, and higher labor costs. Achieving both efficiency and product reliability in competitive markets requires advanced automation solutions.
Reducing Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Energy-intensive drying and forming processes contribute significantly to production costs and carbon emissions. Meeting sustainability regulations while controlling operational expenses is a growing concern, especially as environmental compliance becomes a decisive factor in market competitiveness.
Building Sustainable Egg Tray Production with Beston Group
Beston Group offers pulp molded egg tray machine that directly addresses these industry challenges:
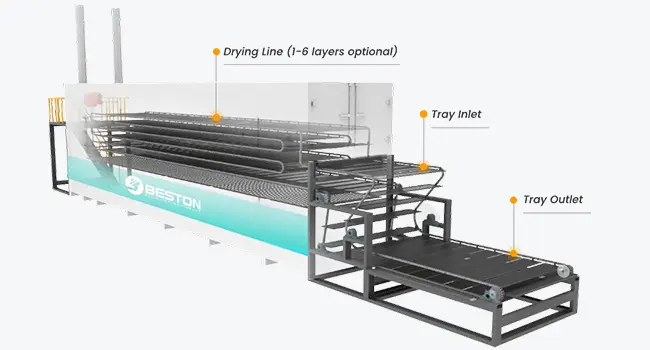
Consistent Tray Quality and Enhanced Strength
Precision forming combined with multi-layer metal drying using hot air circulation ensures every tray maintains consistent shape and robust structural integrity. This reduces deformation and breakage during transportation, protecting eggs throughout the supply chain and minimizing losses for producers and distributors.
Higher Production Efficiency with Automation
Automated molding and stacking increase throughput while maintaining uniform tray quality. By reducing human error and ensuring consistent dimensions and density, producers can reliably deliver high-quality trays, stand out in competitive markets, and scale operations without compromising product standards.


Lower Energy Costs and Environmental Impact
Energy-efficient drying and heat recovery significantly reduce operational costs while maintaining consistent production. This allows producers to meet sustainability requirements, decrease carbon footprint, and align with global trends in environmentally responsible manufacturing.
Conclusion
The global egg industry is expanding, increasing the demand for pulp molded egg trays that ensure safe transport, operational efficiency, and sustainability. As trays evolve from simple packaging to critical logistics components, investing in modern production capacity becomes essential for maintaining quality, controlling costs, and securing long-term market competitiveness.
